How to Configure Long-Term Memory in AI Agents: A Practical Guide to Persistent Context
As AI agents become increasingly sophisticated, one of the most significant challenges developers face is maintaining context beyond a single conversation session. Traditional chatbots reset their memory after each interaction, forcing users to repeat information and losing valuable context. Long-term memory systems solve this problem by enabling AI agents to remember and learn from past interactions, creating more personalized and effective user experiences.
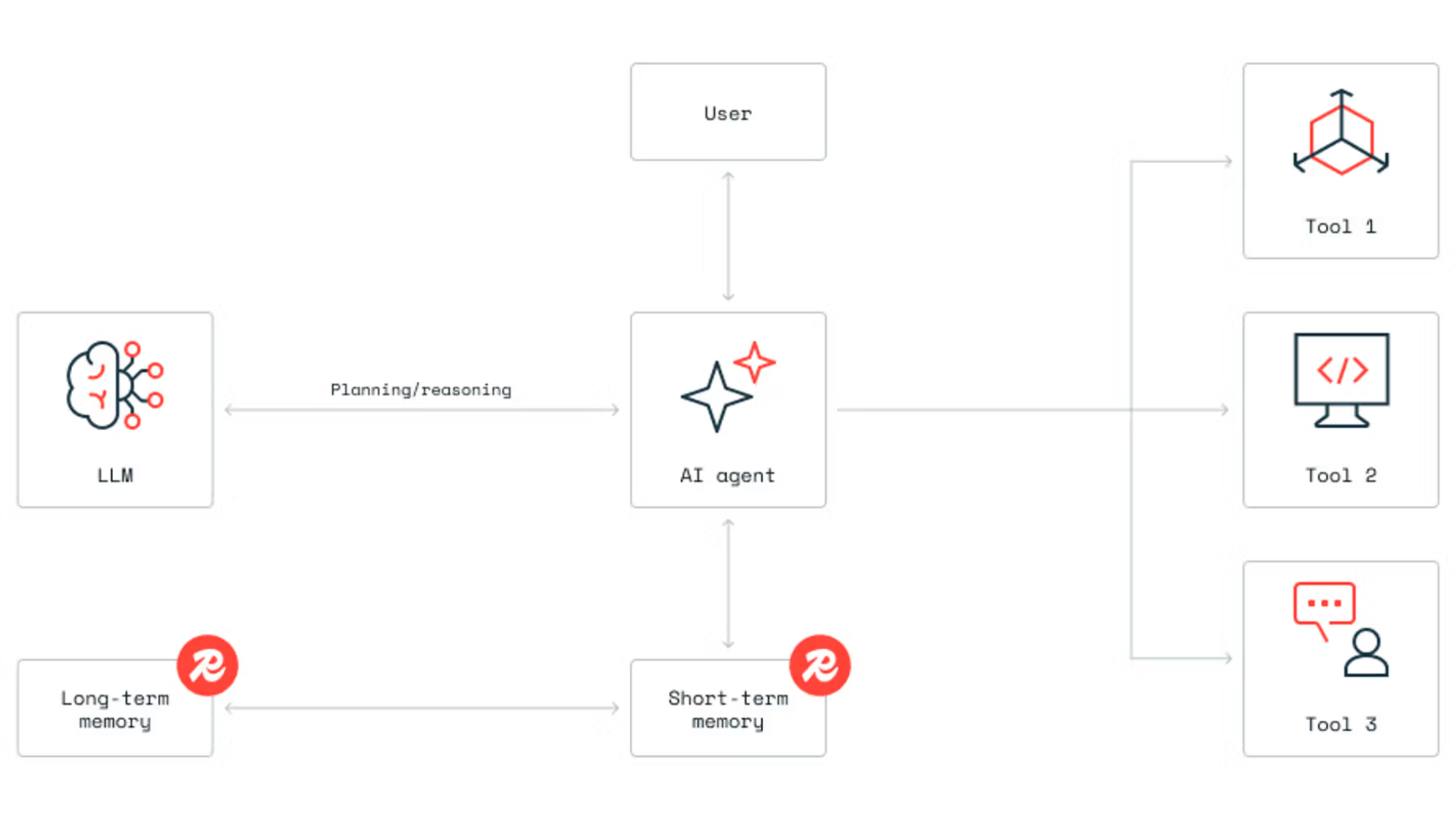
At Asycd, we've implemented a sophisticated long-term memory architecture for Asyra AI that seamlessly bridges short-term conversational context with persistent vector-based storage. This approach ensures that every interaction builds upon previous conversations without impacting latency significantly.
Understanding Long-Term Memory Architecture
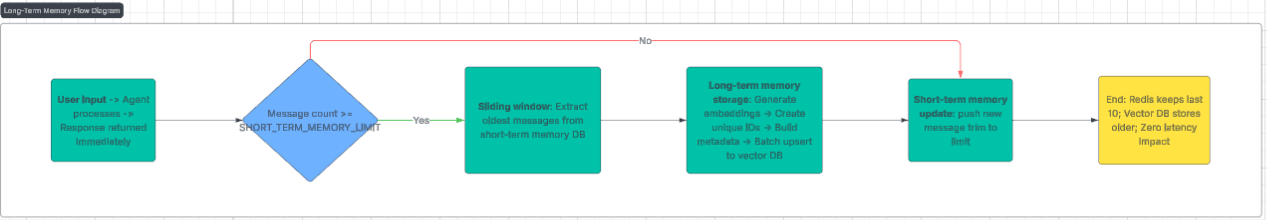
Asyra AI Message Ingestion Process for Long Term Memory
Long-term memory in AI agents operates on a two-tier system: short-term memory for immediate context and long-term memory for persistent storage. In Asyra AI, we maintain the last 10 messages in Redis for fast access during active conversations. When this threshold is reached, older messages are automatically archived to a vector database, preserving conversation history while keeping the system responsive.
The key innovation lies in how we structure this transition. Each conversation exchange is embedded using OpenAI's text-embedding model (can utilize any desired embeddings model) and stored with rich metadata including timestamps, question-answer pairs, and conversation context. This allows the system to retrieve relevant past conversations when users reference previous discussions, even weeks or months later.
Our implementation uses a hybrid approach combining Redis for short-term storage and Upstash Vector for long-term persistence. When a new message arrives and the short-term memory limit is reached, the system:
1. Extracts the oldest conversation from Redis before it's trimmed
2. Generates embeddings for the combined question-answer pair
3. Stores in vector database with comprehensive metadata including datetime, conversation type, and source information
The system automatically handles the migration process in the background, ensuring zero impact on response latency.
# Check if adding would exceed short-term memory limit
current_count = redis_client.llen(CONVERSATION_HISTORY_KEY)
if current_count >= SHORT_TERM_MEMORY_LIMIT:
# Calculate messages to archive
messages_to_archive = (current_count + 1) - SHORT_TERM_MEMORY_LIMIT
# Get oldest messages before trimming
oldest_messages = get_oldest_messages(messages_to_archive)
# Archive to long-term memory
await push_to_long_term_memory(oldest_messages)
Benefits and Applications
Long-term memory transforms AI agents from reactive tools into proactive assistants that understand user preferences, conversation history, and context over time. For businesses, this means:
Personalized Experiences: The AI remembers user preferences, past questions, and interaction patterns, allowing for increasingly tailored responses.
Contextual Continuity: Users can reference previous conversations naturally ("What did we discuss about X last week?") without needing to re-explain context. This can be achieved using time-based filtering on the vector database? Timestamped embeddings allow us to filter conversation history in this manner.
Improved Efficiency: By maintaining conversation history, the AI can provide more accurate answers and reduce redundant explanations.
Scalable Knowledge: As conversations accumulate, the system builds an organizational knowledge base that improves over time.
Mission-Critical Considerations
Implementing long-term memory requires careful attention to several critical factors:
Privacy and Security: Conversation data must be encrypted and stored securely. We implement strict access controls and ensure all data complies with privacy regulations.
Performance Optimization: Memory retrieval must not impact response times. Our background processing ensures conversations are archived asynchronously, maintaining reasonable response times.
Data Management: With potentially thousands of conversations, efficient filtering and retrieval become essential. We use type-based filtering to separate conversation history from knowledge base content, ensuring searches remain fast and relevant.
Cost Management: Vector storage and embedding generation have associated costs. Our tiered approach—keeping recent conversations in Redis and archiving older ones—balances functionality with cost efficiency. RAG on a vector database of conversation messages is as inexpensive as any other RAG process.
Metadata Preservation: Timestamps, conversation context, and source information are crucial for accurate retrieval. We preserve comprehensive metadata to enable precise context matching.
# Standard metadata structure for conversation vectors
metadata = {
"type": "conversation_history",
"date": msg_time,
"question": msg['question'],
"answer": msg['answer'],
"source": "conversation_history"
}
The Asycd Approach
At Asycd, we've built Asyra AI's long-term memory system to be both powerful and practical. Our implementation demonstrates how modern AI agents can maintain context across sessions while respecting performance, privacy, and cost constraints. The system automatically handles the complexity of memory management, allowing developers to focus on building better user experiences.
For organizations looking to implement similar systems, the key is finding the right balance between memory depth and system performance. Our architecture provides a blueprint for scalable, efficient long-term memory that enhances AI capabilities without compromising speed or reliability.